How to Use Pogo Pins: Learn Expert Tips and Techniques to Maximize Efficiency with Pogo Pins in Your Prototyping Phase | Electronic Designs
Introduction
Pogo Pins are crucial in modern electronic design. Despite their simple appearance, they play a vital role in electrical connections and signal transmission. Their spring-loaded design allows for reliable connections between devices, making them ideal for testing, programming, and data transfer.
This blog will dive into how Pogo Pins work and their various uses. Whether you’re a beginner or a pro, you’ll find valuable insights to help you understand and utilize these small but powerful connectors.
1. Basics of Pogo Pins
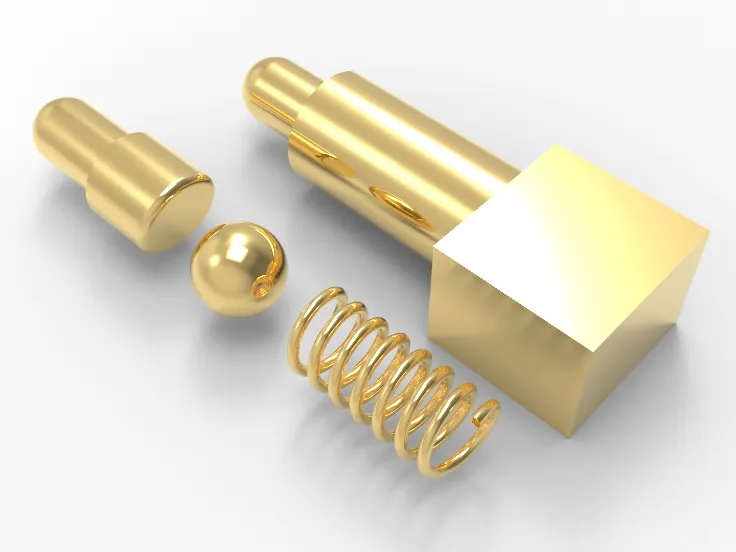
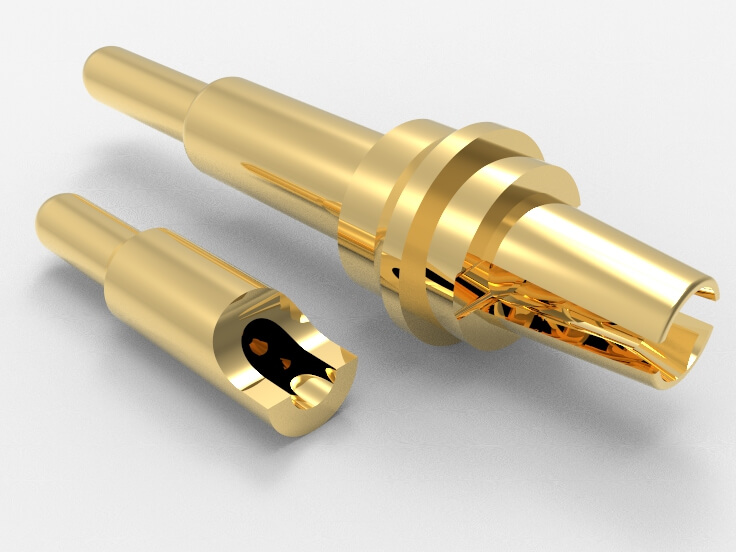
Pogo Pins are common connectors in electronics, working based on the physical properties of springs and precise design. They’re made of conductive materials and feature one or more spring structures connected to a circuit board.
1.1 Key Principles:
- Spring Structure: Made from high-elasticity metals like stainless steel, springs store energy when compressed and rebound to maintain stable contact and connection.
- Conductivity: The main function is to provide electrical connection between devices. Conductive parts are located at the bottom and top of the springs, connecting with the circuit board.
- Precision Design: Ensures stable connection and signal transmission. Includes material choice, spring tension, contact surface coating, and size.
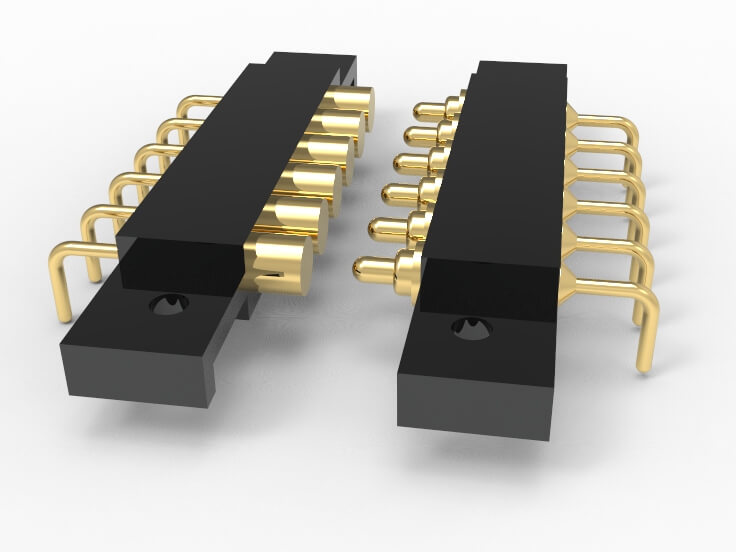
- Applications: Widely used in test sockets, programming interfaces, and data ports. Ideal for environments requiring frequent connect/disconnect, such as mobile devices and industrial equipment.
Pogo Pins offer reliable electrical connections and signal transmission, crucial in modern electronics for efficient communication and operation.
2. Using Pogo Pins: Steps and Tips
2.1 Correct Usage:
2.1.1 Choosing the Right Pogo Pins:
- Understand Your Needs: Select based on application (testing, programming, etc.), considering contact force, current capacity, length, and mounting.
- Correct Specifications: Ensure compatibility with your circuit board or device, including diameter, length, and head design.
2.1.2 Installing Pogo Pins:
- Preparation: Confirm the layout and installation positions.
- Installation Tips: Use appropriate tools (e.g., soldering equipment) and ensure secure soldering without overheating.
2.1.3 Connecting and Testing:
- Connect Devices: Align Pogo Pins with test points or connectors and apply pressure for good electrical contact.
- Testing: Use test equipment to check electrical connections, programming, or data transfer. Ensure stable connections and signal quality.
2.1.4 Maintenance and Precautions:
- Regular Checks: Inspect connections and cleanliness regularly to avoid oxidation or contamination.
- Avoid Overload: Prevent exceeding rated current and pressure to avoid damage.
2.1.5 Reference and Support:
- Technical Documents: Review technical specifications and installation guides.
- Manufacturer Support: Consult with manufacturers for additional support and advice.
2.2 Lesser-Known Efficient Tips:
- Optimizing Spring Force: Adjust spring tension for different pressure requirements, improving stability and efficiency in high-frequency and high-speed data transfer.
- High-Temperature Use: Choose materials and coatings that withstand high temperatures for stable performance.
- Vibration Prevention: Use shock-absorbing mounts or techniques to minimize external vibrations affecting connections.
- Special Environments: For outdoor or polluted settings, select dustproof and waterproof designs, and maintain cleanliness.
- Automation: Implement automated testing for rapid insertion and testing, boosting production efficiency and precision.
Master these techniques to efficiently select, install, and use Pogo Pins, ensuring high performance and reliability in complex electronic applications.
3. Applications of Pogo Pins
Here’s a quick look at how Pogo Pins are used across various fields, highlighting their importance in modern technology and industry.
3.1 Medical Devices:
- Usage: Connects electrical components and transfers data.
- Installation: Make sure the circuit board has a solid connection to prevent any signal issues.
- Maintenance: Regularly check for oxidation or dirt and clean as needed. Test each connection’s resistance with precision instruments to ensure stable signal transmission.
3.2 Consumer Electronics:
- Usage: Common in charging and data ports.
- Installation: Align Pogo Pins accurately to prevent poor insertion.
- Maintenance: Monitor for wear and replace damaged pins. Simulate various scenarios to test performance stability.
3.3 Automotive Electronics:
- Usage: Connect modules in-vehicle systems.
- Installation: Ensure secure connections to avoid issues from vibrations.
- Maintenance: Frequently inspect for any loose pins and tighten or swap them out if needed. Test performance in simulated driving conditions.
3.4 Communication Devices:
- Usage: Provides quick connections between modules.
- Installation: Insert Pogo Pins in the correct direction to avoid damage.
- Maintenance: Clean contact points regularly to prevent dust and dirt buildup. Check signal stability with an oscilloscope to ensure smooth transmission.
3.5 Industrial Automation:
- Usage: Connects robots and controllers.
- Installation: Ensure precise alignment to reduce mechanical errors.
- Maintenance: Check contacts regularly for stability under heavy loads. Test durability and reliability in real-world operations.
3.6 Computer Hardware:
- Usage: Connects different circuit boards or modules.
- Installation: Ensure consistent insertion depth to avoid poor contact.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean Pogo Pins to prevent dust accumulation. Use comprehensive test equipment to check electrical performance.
3.7 Embedded Systems:
- Usage: Used for testing and programming interfaces.
- Installation: Align Pogo Pins precisely for stable contact.
- Maintenance: Check for physical damage and clean regularly. Test performance by simulating real-world conditions.
3.8 Aerospace Equipment:
- Usage: Provides reliable electrical connections in high-stress environments.
- Installation: Ensure stability under high vibration and temperature conditions.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect contact points to avoid performance degradation. Conduct environment simulations to ensure reliability under extreme conditions.
Conclusion
Using Pogo Pins is crucial for enhancing connection stability and reliability in electronic products. Mastering Pogo Pin techniques can greatly boost both your device’s performance and production efficiency. Whether you’re building prototypes or final products, getting good with Pogo Pins can set you apart from the competition.
Start applying these key techniques to optimize your electronic designs! Whether you’re an engineer or product developer, mastering Pogo Pins will set you apart in a competitive market. Follow our blog for more practical tech insights and industry updates. For questions, professional advice, or Pogo Pins, contact my CFT team—we’re here to help!